

Go to Arm.com and download the Linux version, extract it in ~/armsystem/toolchain directoryĪdd the location to the PATH environment variable: # export PATH=/home/developer/armsystem/toolchain/gcc-arm-none-eabi-7-2017-q4-major/bin/:$PATH The first thing we need to install is a cross toolchain for ARM. To check if qemu is installed correctly run # qemu-system-arm -M ? Now run configure again and check that SDL support is reported yes More packages needed: # sudo apt-get install libpixman-1-dev I’m using Ubuntu and it’s very easy to install the missing parts, for example, I got the following message: ERROR: glib-2.22 gthread-2.0 is required to compile QEMUĪfter searching Google install the required packages # sudo apt-get install libglib2.0-dev zlib1g-dev If you get error messages you need to install missing packages. The last step checks if your system meets all qemu requirements. You can install binary version but it is better to download and build Qemu from source because we can use the source to simulate a new hardware. In this tutorial, I’ll cover the steps to build a complete system including kernel, filesystem, and application Qemu – Building from source
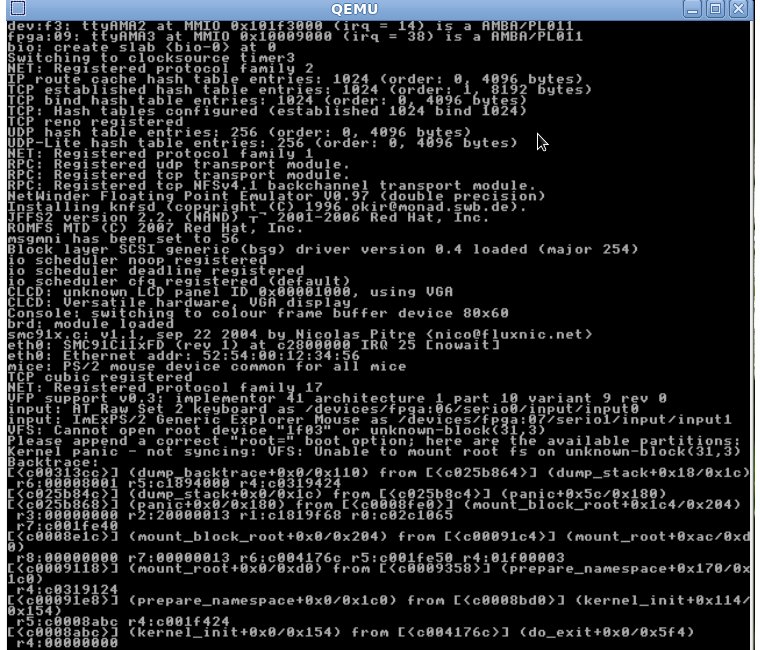

Qemu simulates many boards including hardware, interrupts, networking and more. In my Embedded Linux courses, I’m using Qemu to simulate a Linux system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
